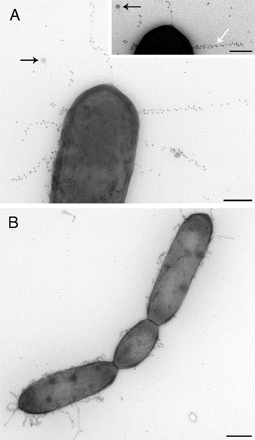
Light microscopy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N (a, b) and PEN (c, d).

Download scientific diagram | Light microscopy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N (a, b) and PEN (c, d). Cells suspended in PBS and mixed with ammonium sulfate 0.02 M, pH 6.8 are shown in a and c, arrows from publication: The effect of cell surface components on adhesion ability of Lactobacillus rhamnosus | The aim of this study was to analyze the cell envelope components and surface properties of two phenotypes of Lactobacillus rhamnosus isolated from the human gastrointestinal tract. The ability of the bacteria to adhere to human intestinal cells and to aggregate with other | Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Adhesion and Exopolysaccharide | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
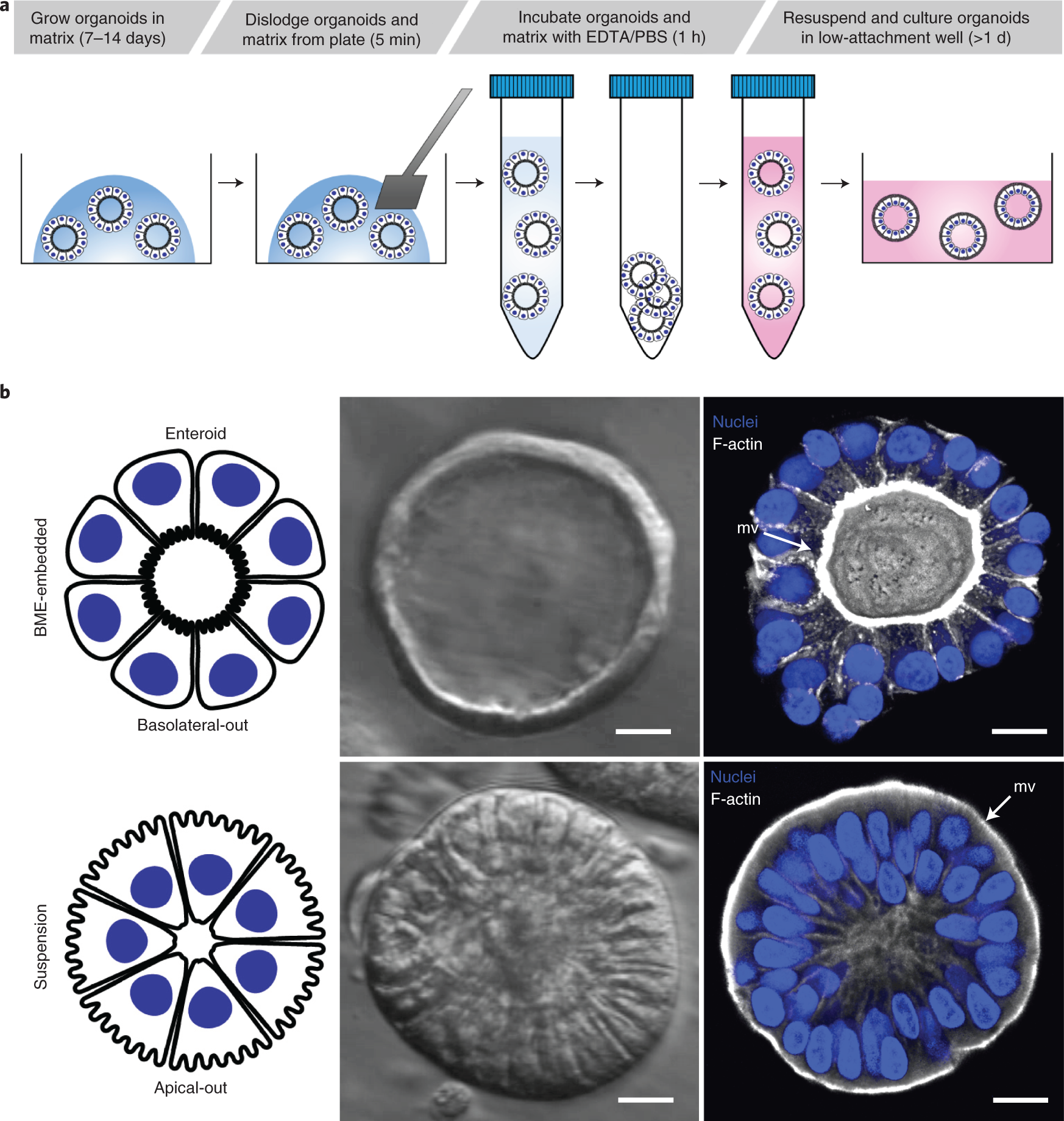
Controlling the polarity of human gastrointestinal organoids to
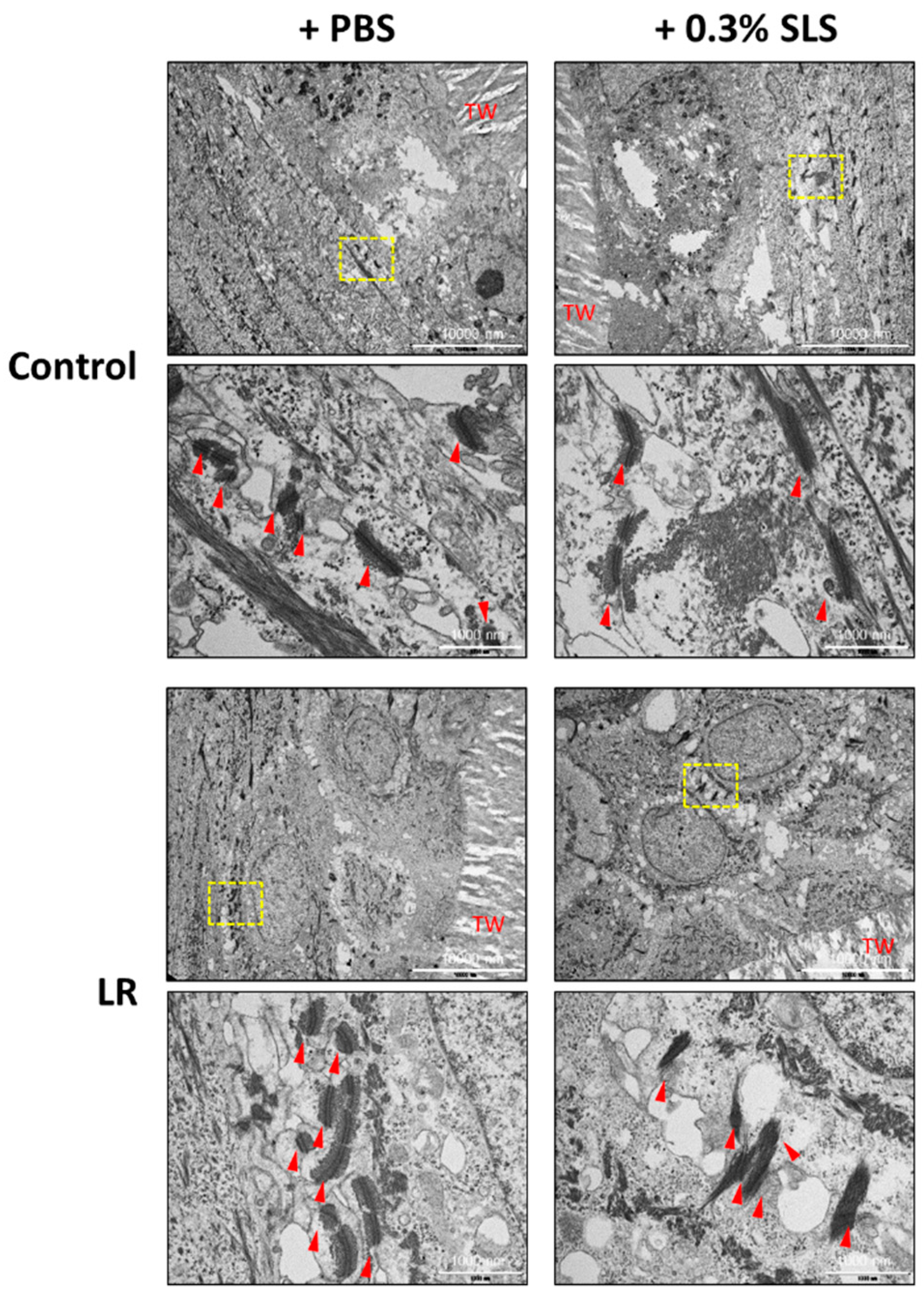
IJMS, Free Full-Text
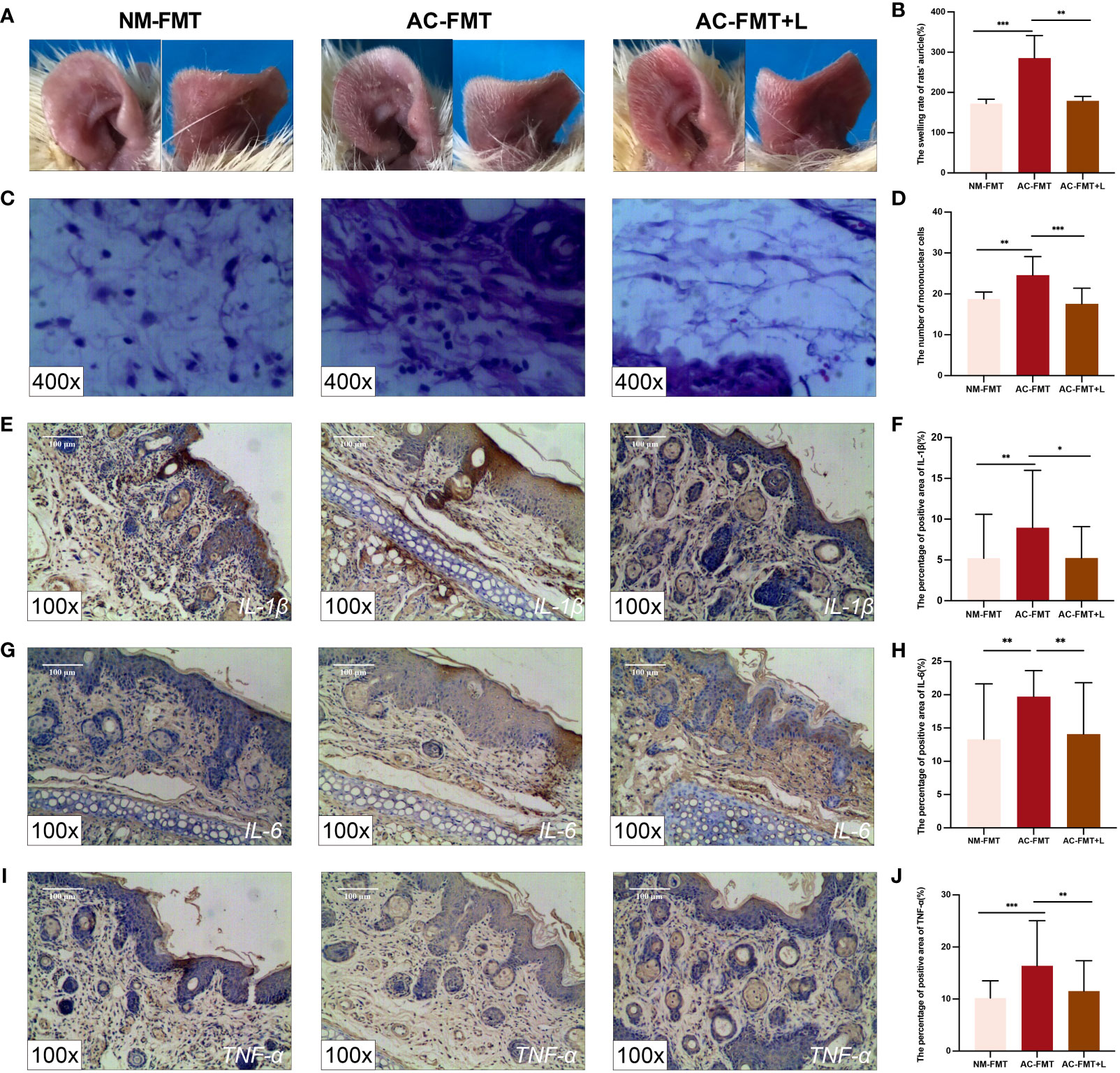
Frontiers Lactobacillus rhamnosus ameliorates acne vulgaris in

Wnt5A Signaling Regulates Gut Bacterial Survival and T cell

Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text
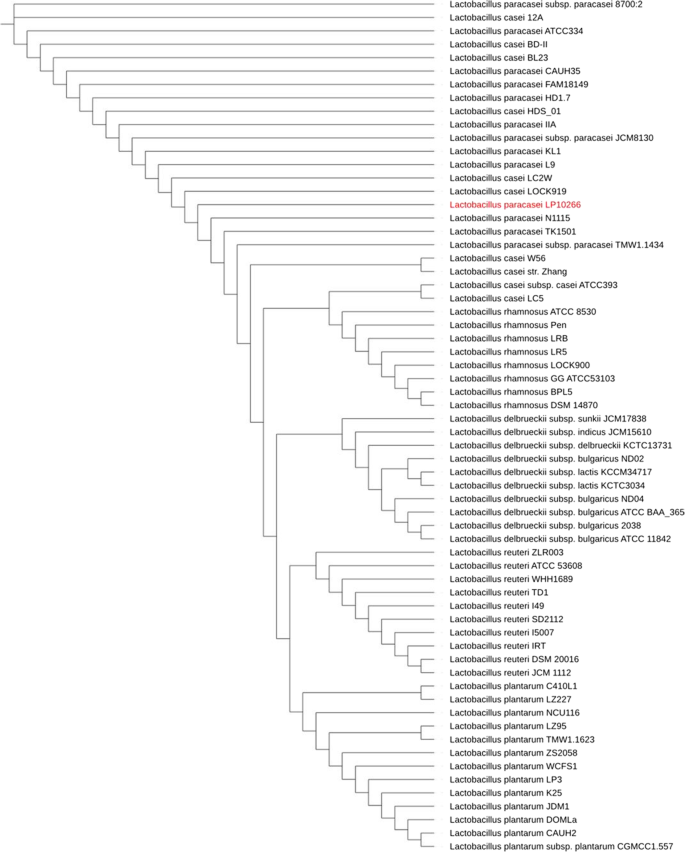

Characterization of a bacterial strain Lactobacillus paracasei

In vitro adhesion of Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N and PEN to HT-29

PDF) Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus Pen, a

Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Genomic and Phenotypic Stability in an
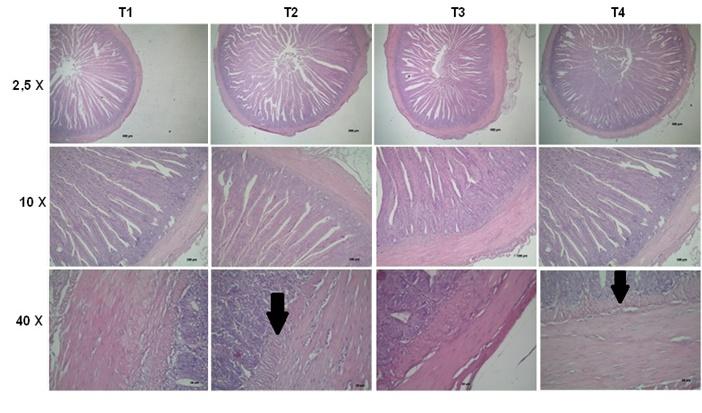
Mixed probiotic/anti-mycotoxin additive (Saccharomyces cerevisiae
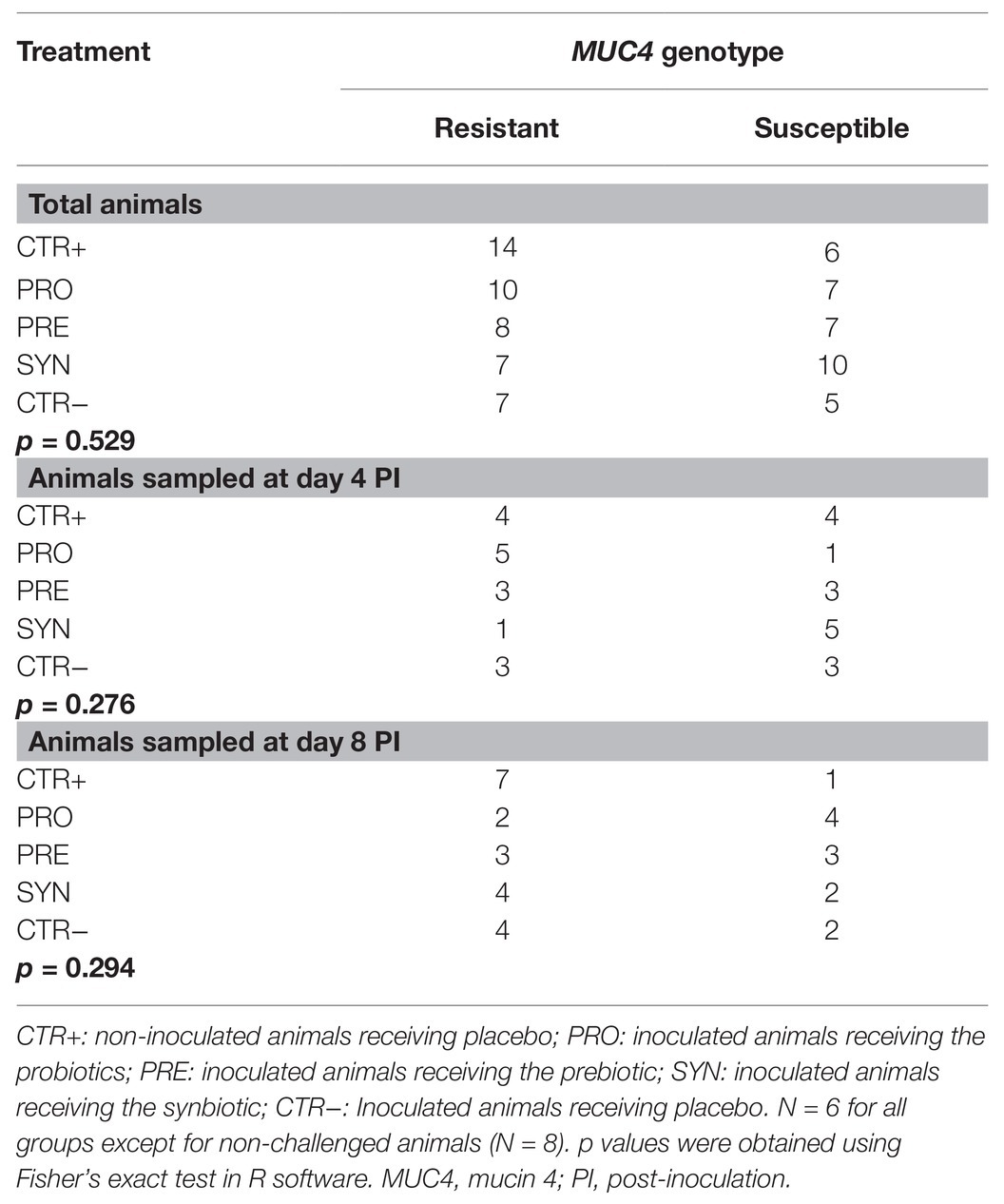
Frontiers Effects of the Administration of Bifidobacterium
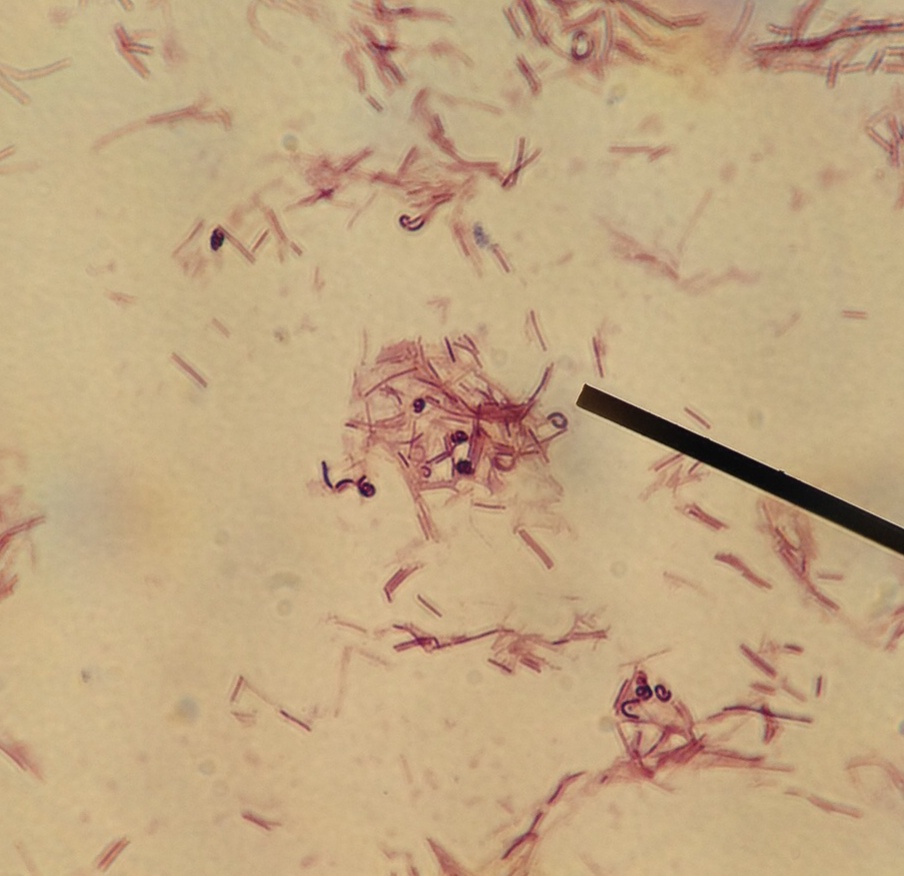
File:Lactobacillus rhamnosus-LSU lab (Dr. Karen Sullivan).jpg

Complete genome sequence of Lactobacillus rhamnosus Pen, a

Light microscopy of Lactobacillus rhamnosus E/N negatively stained