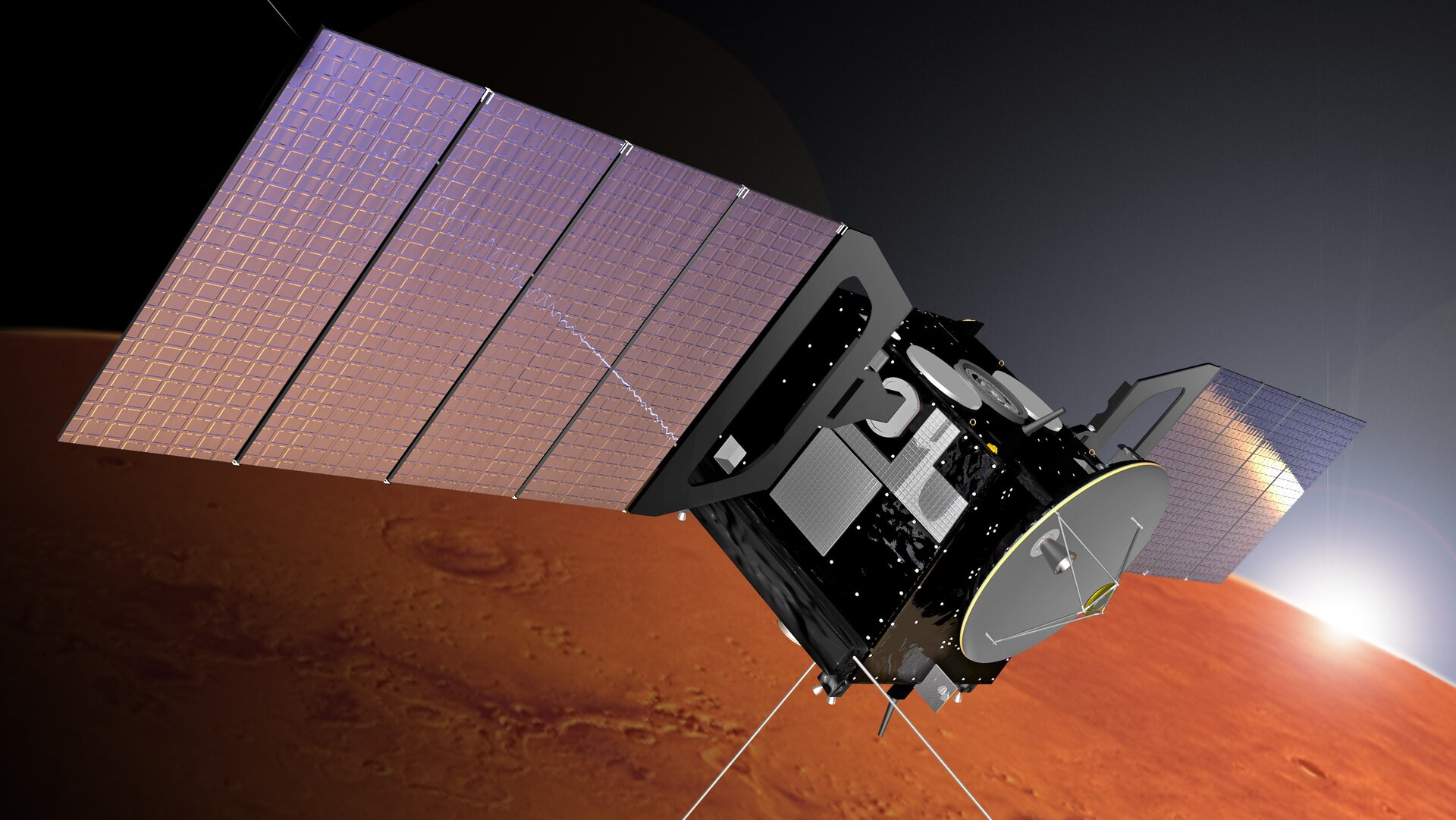
Spacecraft design The lessons learnt from the Mars Express mission

Download scientific diagram | Spacecraft design The lessons learnt from the Mars Express mission, with its Beagle Lander, indicated that a landing mission without an active propulsion system has a high degree of risk in losing the mission. This seems to be the case for the Beagle descent mission. Based on this assumption, ESA decided to investigate two landing philosophies, thus: 1. Solid rocket motor braking manoeuvre, supported by a liquid propulsion system with capsuled airbag solution 2. Soft landing with liquid propulsion and a lower floor airbag damping system. from publication: Propulsion Technologies -Present Status and Future Needs for Exploration | Propulsion is an indispensable element for all future space challenges. European concentration in the last 30 years in this sector was focused mainly on launcher and satellite propulsion applications. Now, Europe's future view for exploration on the Moon and Mars missions | Propulsion, Europe and Robotics | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

XPRIZE Gives Moon Express a GO for 2017 Launch to Land First

Mars orbiter relies on 'science friction
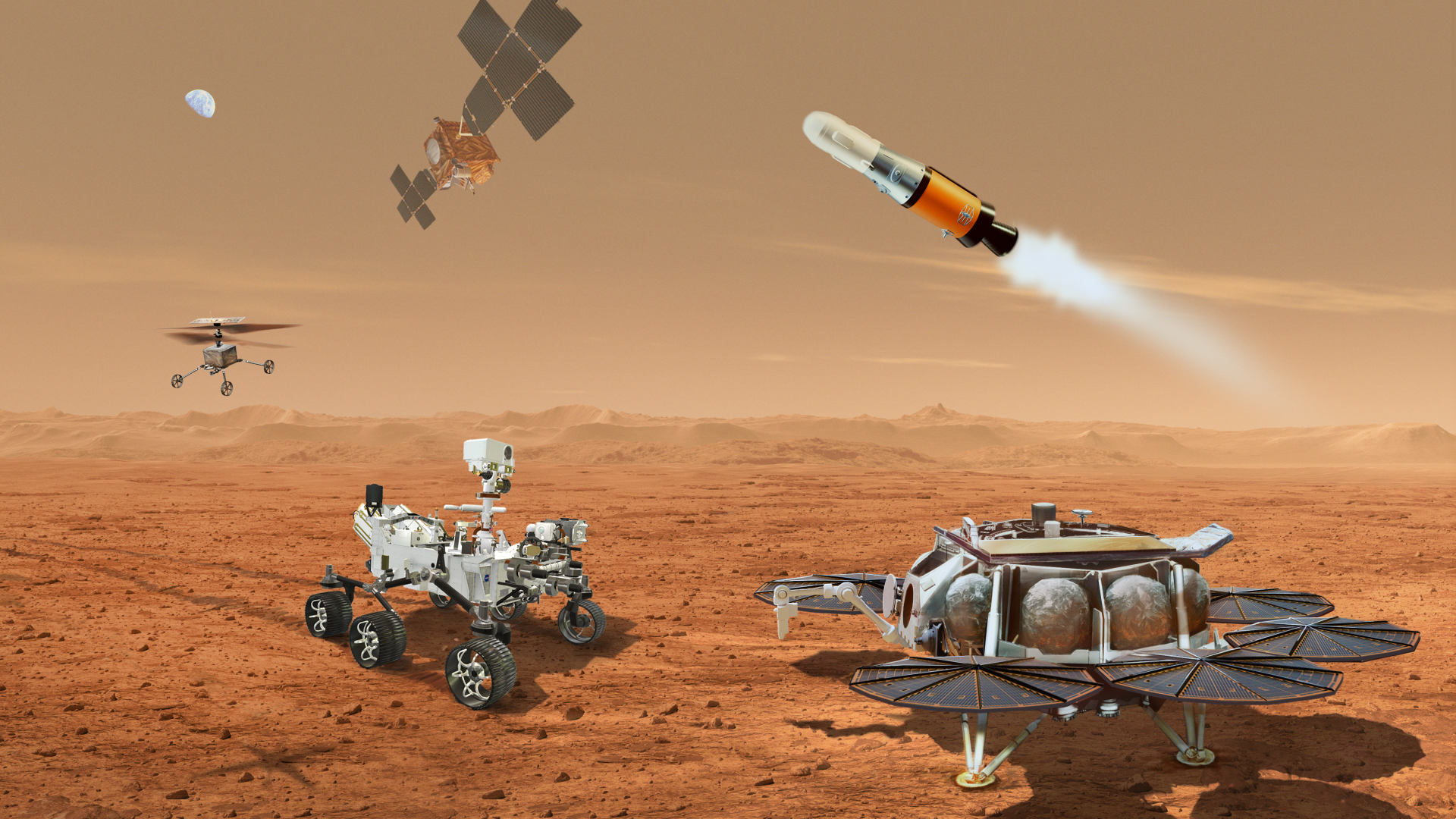
What's ahead in returning samples from Mars?
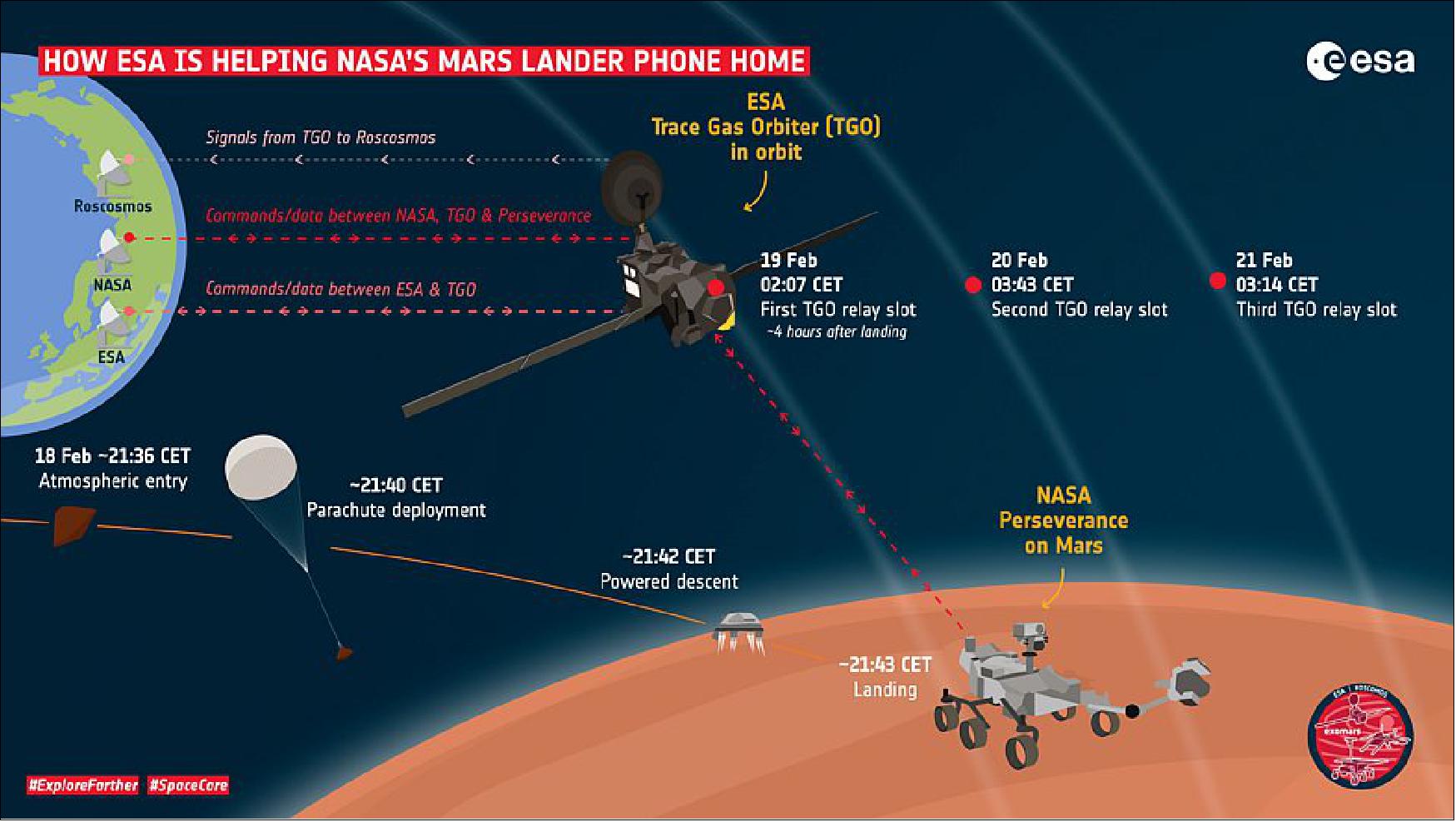
Mars Express - eoPortal

M5 — Mars Magnetospheric Multipoint Measurement Mission: A multi
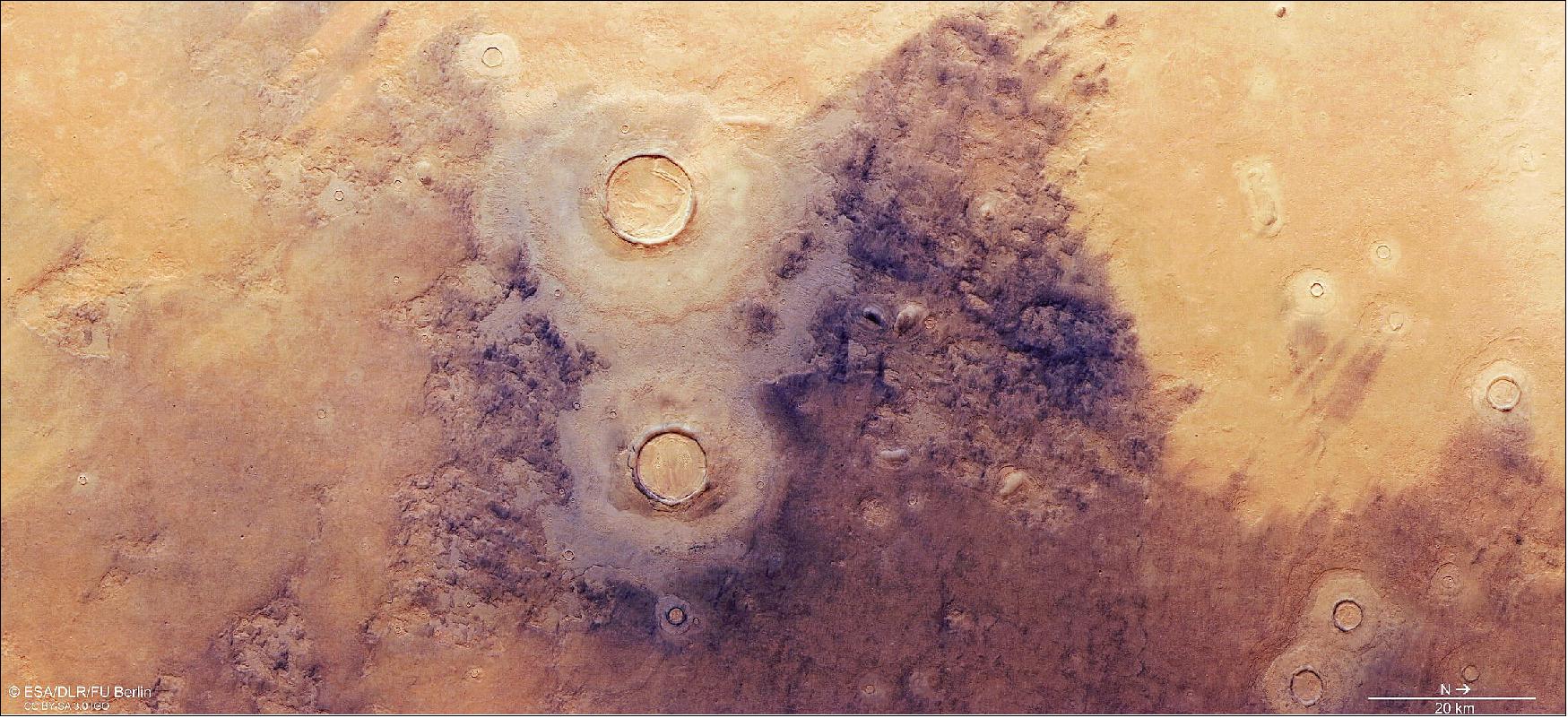
Mars Express - eoPortal

Red Planet Retrospective: NASA's 30-Year Mission to Mars - Bloomberg

ESA - Lessons learnt from Beagle 2 and plans to implement

ISRO's Mars orbiter was made for mission life of six months

Educator Guide: Mission to Mars Unit









