The Glutamatergic Synapse
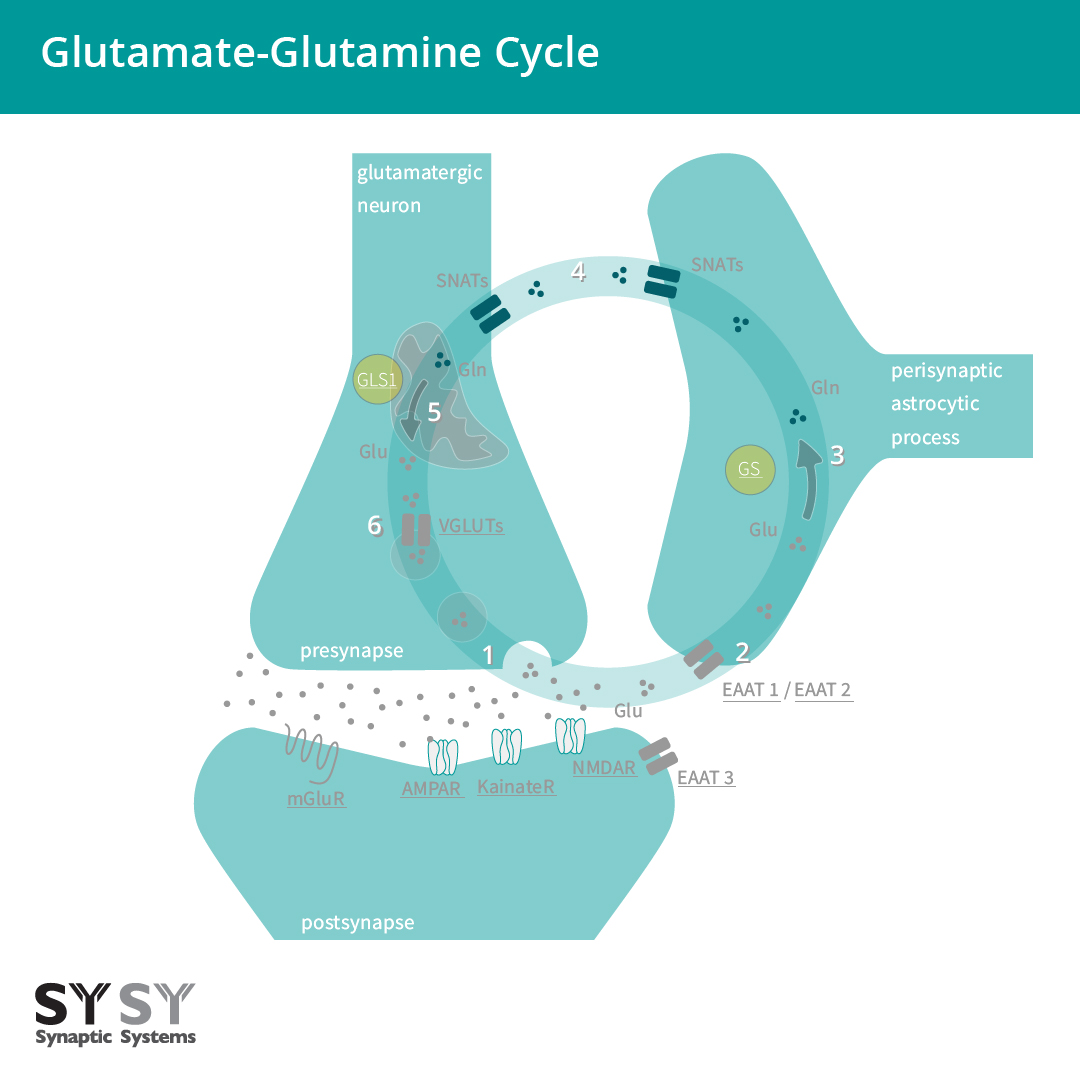
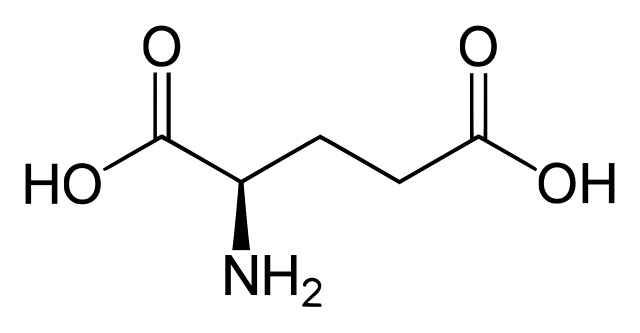
In the mammalian central nervous system (CNS), glutamate is the predominant excitatory neurotransmitter. It is estimated that more than half of all synapses release glutamate and that almost all excitatory neurons in the CNS are glutamatergic.

GABA Enhances Transmission at an Excitatory Glutamatergic Synapse

How do synaptic vesicles accumulate glutamate? – Kompass des Forschungsbereichs Information

Functional synapses between small cell lung cancer and glutamatergic neurons

Presynaptic α2δ subunits are key organizers of glutamatergic synapses

Counting the Number of Glutamate Molecules in Single Synaptic Vesicles
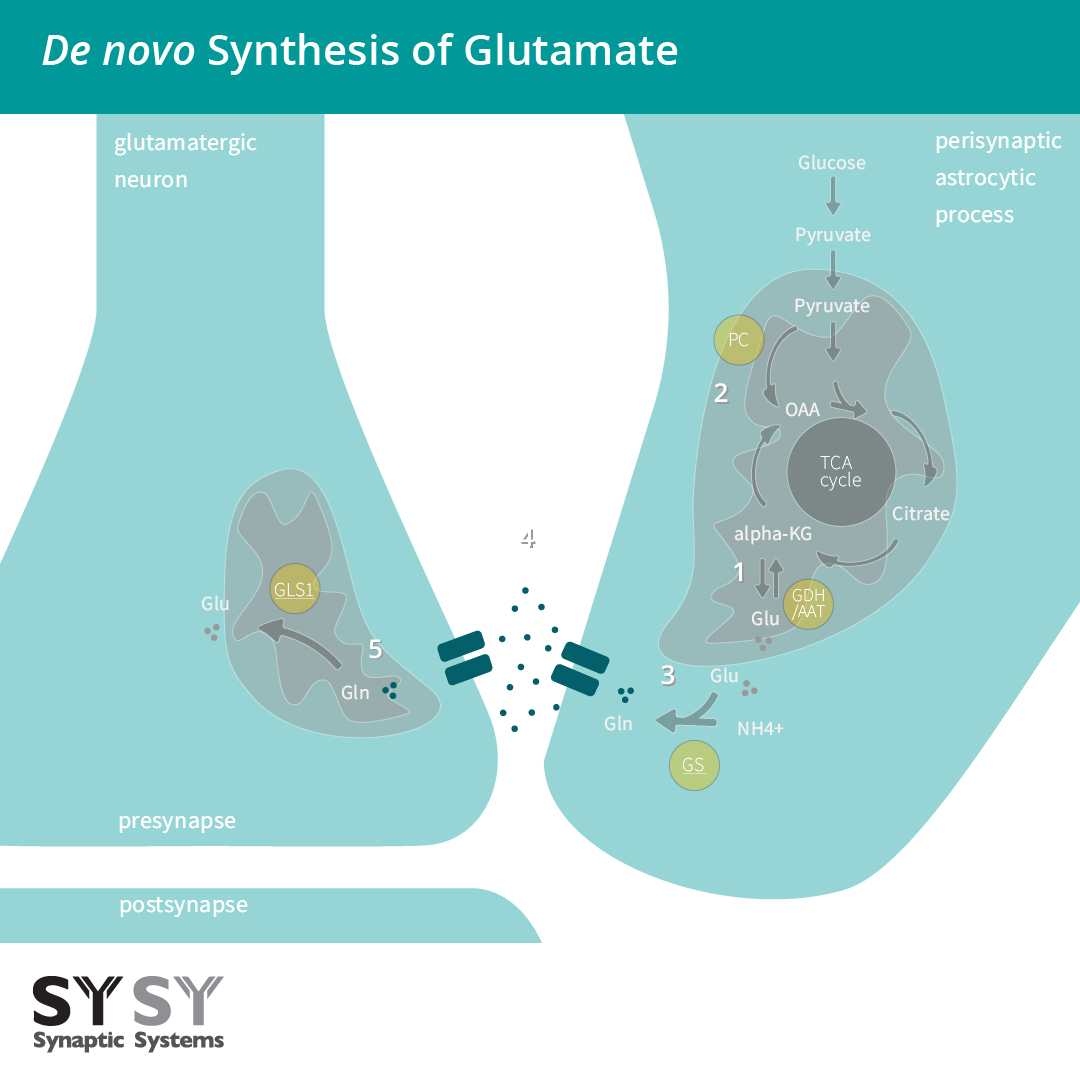
The Glutamatergic Synapse
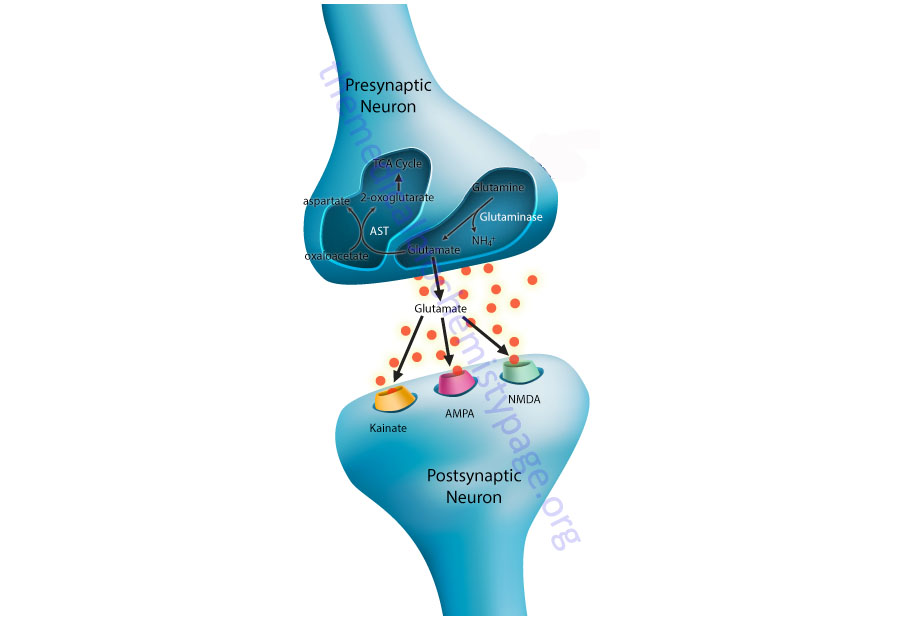
Biochemistry of Nerve Transmission - The Medical Biochemistry Page

The glutamatergic synapse: a complex machinery for information processing

A simplified model of glutamate (Glu) synapse depicting some of the

Figure 1, Schematic drawing of a glutamatergic synapse, with postsynaptic AMPA, NMDA, KA and metabotropic receptors - Jasper's Basic Mechanisms of the Epilepsies - NCBI Bookshelf

Infographic: How a Glutamate Sensor Tracks Synapses

Unique transsynaptic complexes enable long-term synaptic plasticity in a synapse-specific manner