Lactobacillus rhamnosus bacteria, SEM - Stock Image - C037/4516 - Science Photo Library

Lactobacillus rhamnosus bacteria, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). Lactobacillus rhamnosus is particularly useful in probiotics because of its ability to adhere to cells, colonize the intestine, exclude or reduce pathogenic adherence, produce compounds antagonistic to pathogen growth, resist vaginal microbicides and form a normal, balanced flora. STEVE GSCHMEISSNER/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

20+ Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock

20+ Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock
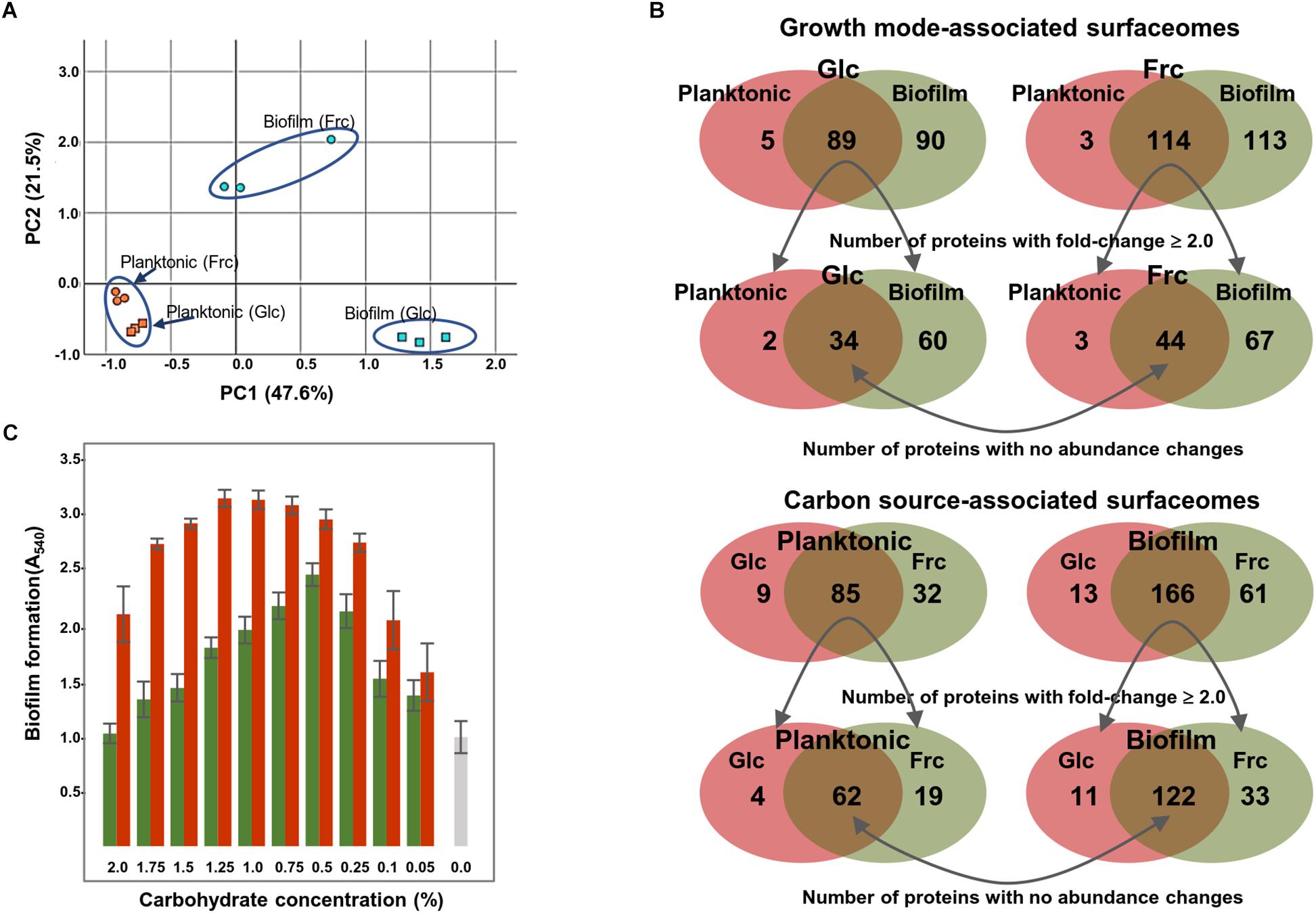
Frontiers Growth Mode and Carbon Source Impact the Surfaceome Dynamics of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG

Microencapsulated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in whey protein and resistant starch matrices: Probiotic survival in fruit juice - ScienceDirect

Microencapsulated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in whey protein and resistant starch matrices: Probiotic survival in fruit juice - ScienceDirect

20+ Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock

Microencapsulated Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG in whey protein and resistant starch matrices: Probiotic survival in fruit juice - ScienceDirect

20+ Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock

Lactobacillus rhamnosus bacteria, SEM - Stock Video Footage - Dissolve

Comparative genomic analysis of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG reveals pili containing a human- mucus binding protein