L-Carnitine ((R)-Carnitine), Co-factor for β-oxidation
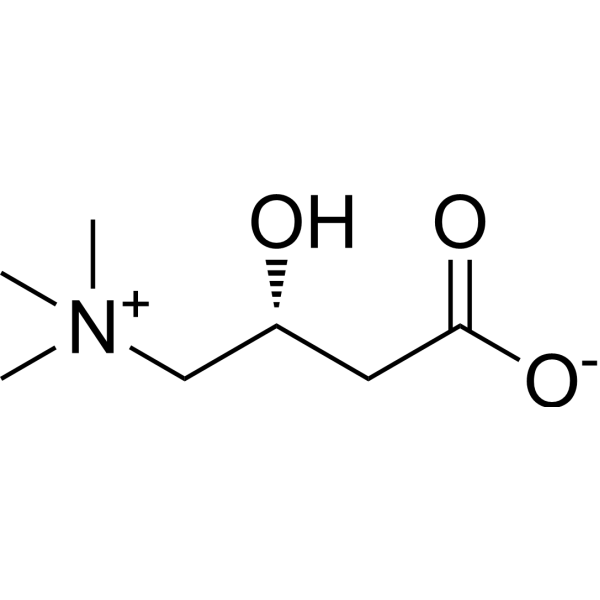
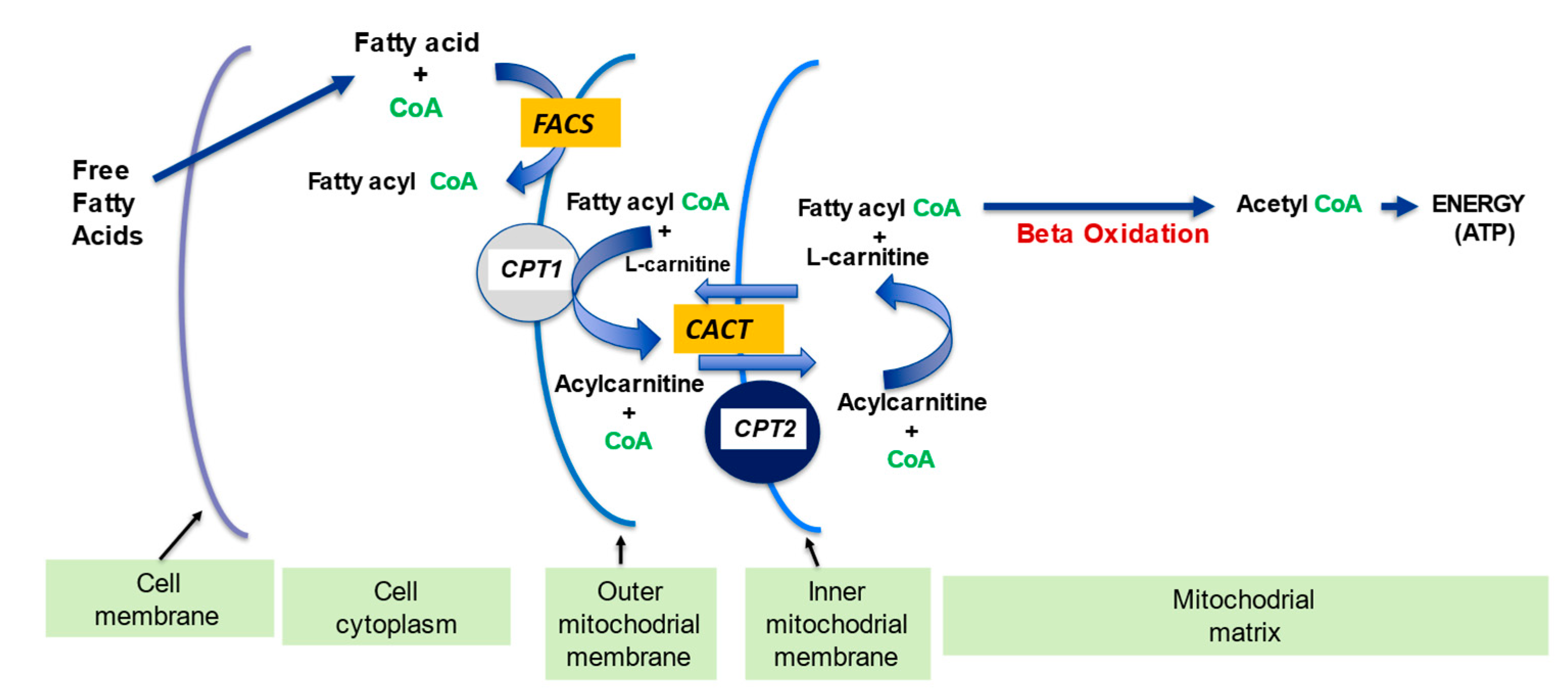
L-Carnitine ((R)-Carnitine), a highly polar, small zwitterion, is an essential co-factor for the mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway. L-Carnitine functions to transport long chain fatty acyl-CoAs into the mitochondria for degradation by β-oxidation. L-Carnitine is an antioxidant. L-Carnitine can ameliorate metabolic imbalances in many inborn errors of metabolism. - Mechanism of Action & Protocol.
Carnitine 500mg (Vegan) - 100 vegetarian free-base liquid capsules

L-Carnitine reduced order ⚡ Blitz-Versand - Gigas Nutrition
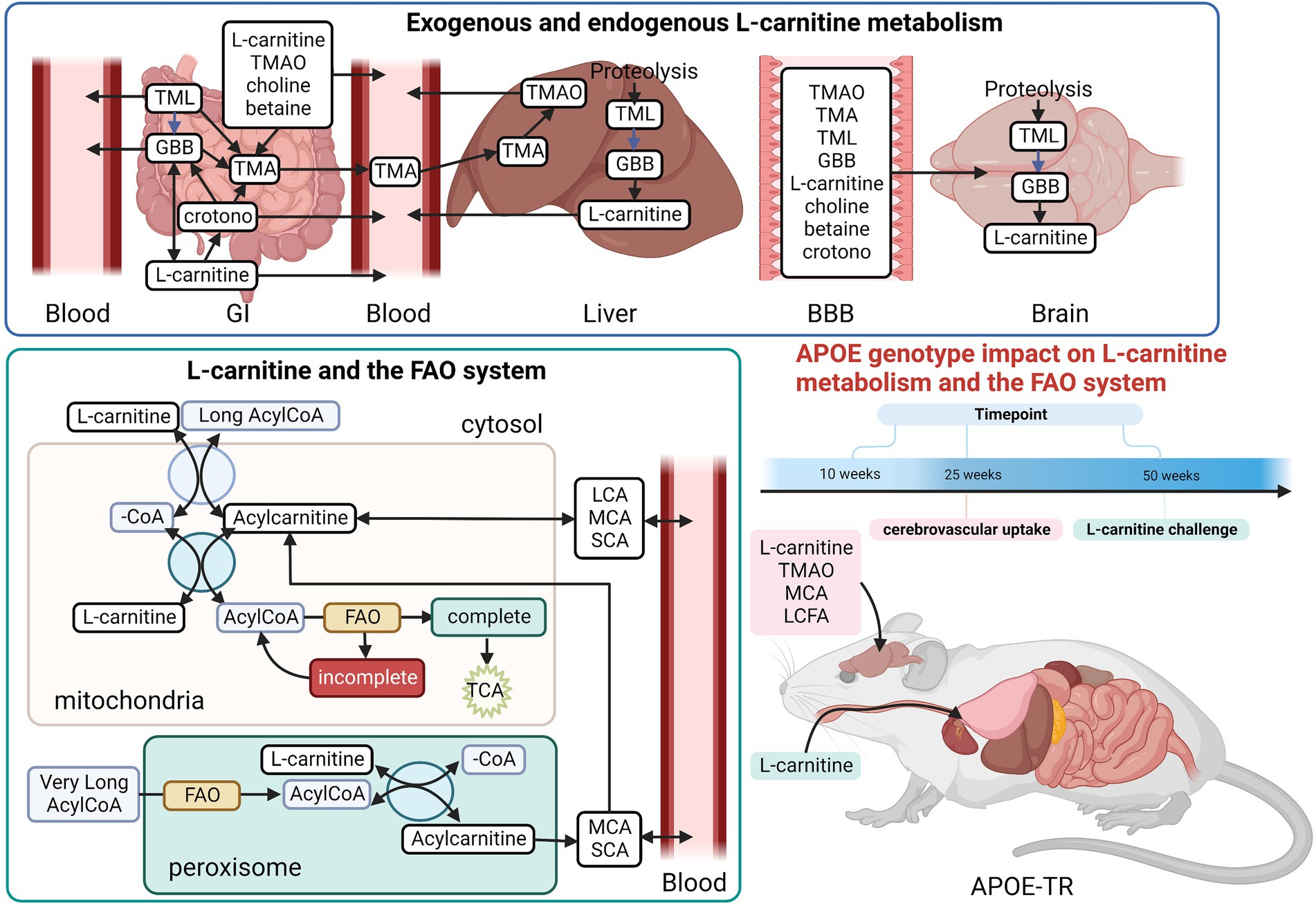
Frontiers Age and APOE affect L-carnitine system metabolites in the brain in the APOE-TR model
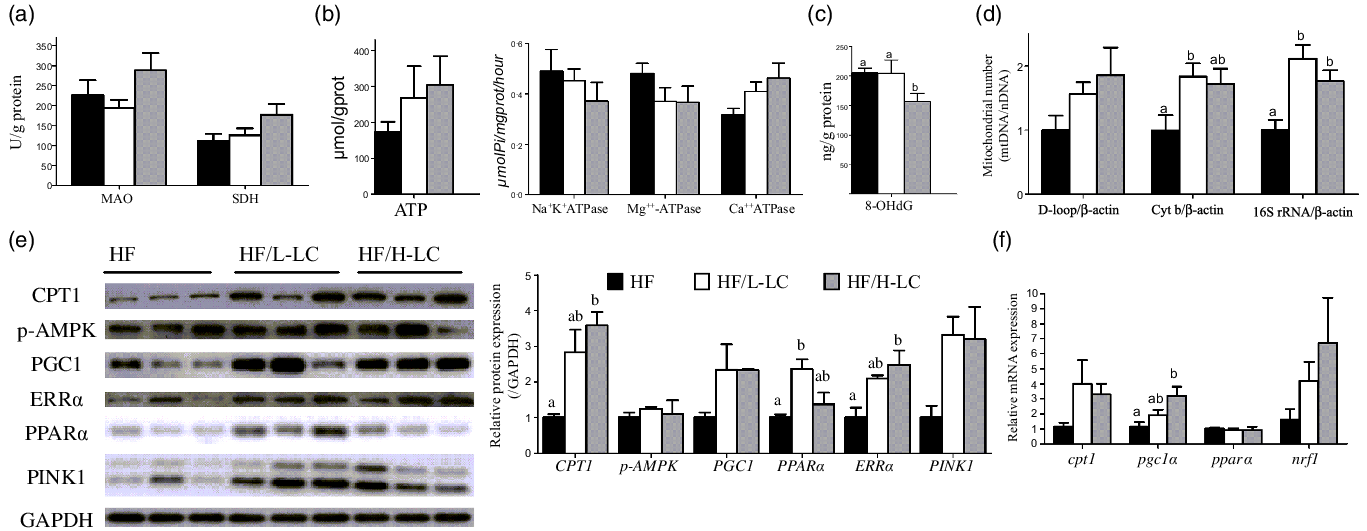
Dietary l-carnitine regulates liver lipid metabolism via simultaneously activating fatty acid β-oxidation and suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in large yellow croaker fed with high-fat diets, British Journal of Nutrition

Carnitine Complex – Naturally Nourished

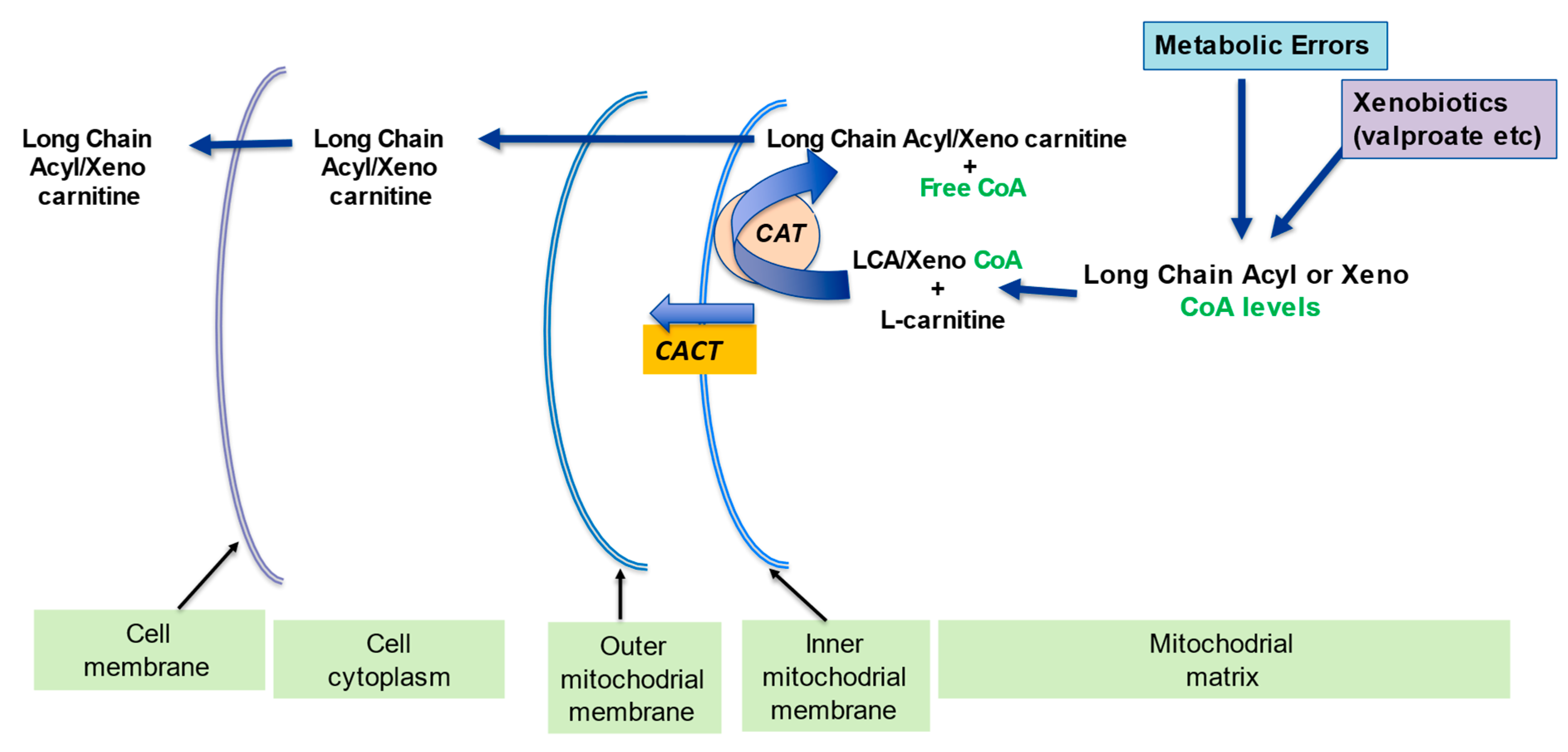
Role of L-carnitine in oxidative metabolism. CoASH, acetyl-CoA; CPT

Acylcarnitines: Nomenclature, Biomarkers, Therapeutic Potential, Drug Targets, and Clinical Trials
L-Carnitine-d9 (chloride)e is the deuterium labeled L-Carnitine chloride. L-Carnitine chloride, a highly polar, small zwitterion, is an essential
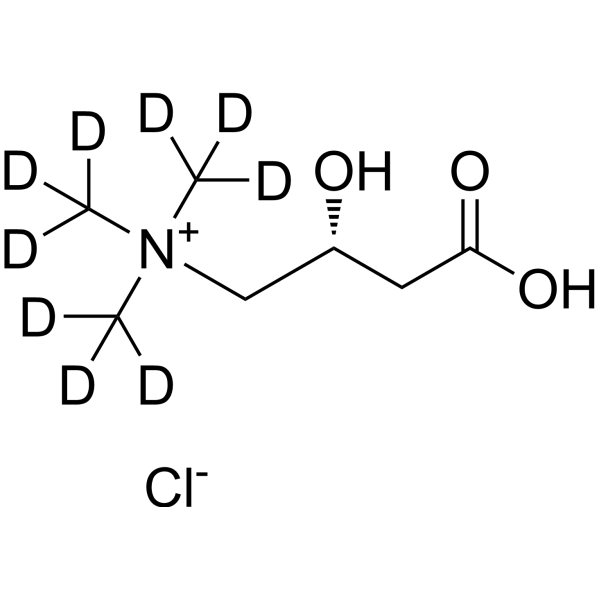
L-Carnitine-d9 chloride
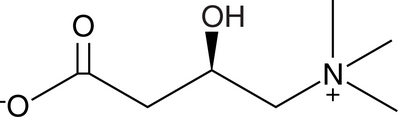
L-Carnitine ((–)-Carnitine, Levocarnitine, R-Carnitine, CAS Number: 541-15-1)
Carnitine promotes recovery from oxidative stress and extends lifespan in C. elegans
IJMS, Free Full-Text

The protective role of l-carnitine on oxidative stress, neurotransmitter perturbations, astrogliosis, and apoptosis induced by thiamethoxam in the brains of male rats
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Frontiers Role of Carnitine in Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Other Related Diseases: An Update
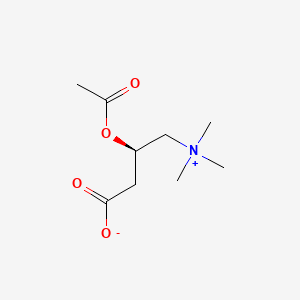
Acetyl-L-carnitine, C9H17NO4